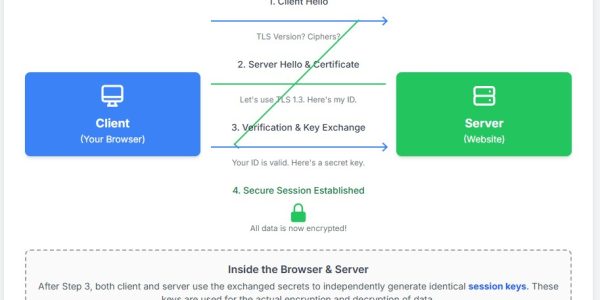
Modern API security has evolved from protecting the “perimeter” to securing the internal business logic. To prevent data breaches in 2026, organizations must move beyond simple API keys and adopt a Zero-Trust architecture that utilizes mTLS, granular Object-Level Authorization (BOLA prevention), and AI-driven behavioral analysis.
At infineural Technologies, our data indicates that while 90% of enterprises use basic authentication, fewer than 20% effectively monitor for Broken Object Property Level Authorization (BOPLA). This guide provides the comprehensive technical steps required to bridge that gap, ensuring your Application Programming Interfaces remain resilient against both automated bots and sophisticated logic-based attacks.
1. The 2026 API Threat Landscape: Beyond the OWASP Top 10
While the OWASP API Security Top 10 remains the gold standard, the entry of AI into the developer stack has introduced new “Entity-Based” threats. Attackers are no longer just looking for SQL injections; they are looking for “leaky” logic.
The Rise of the “Slow Leak” Attack
In our work at infineural Technologies, we’ve observed a shift toward “Slow Leak” exfiltration. Instead of a massive spike in traffic, attackers use legitimate credentials to scrape one record every few seconds. Traditional WAFs ignore this.
- Key Takeaway: You must implement Behavioral Baselining to detect deviations in normal user data-consumption patterns.
2. Authentication and Identity: The Zero-Trust Foundation
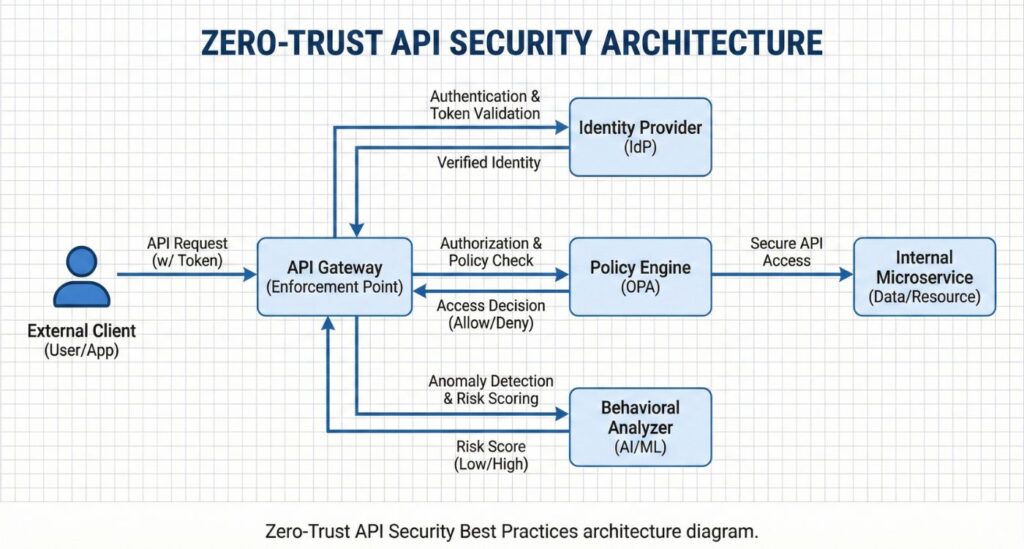
Identity is the new perimeter. If your API Security Best Practices Guide relies solely on API keys, you are at risk.
Implementing OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC)
OAuth 2.0 is an authorization framework, not a security silver bullet. Its security depends on the implementation of “scopes” and “claims.”
- Use OIDC for Identity: Always layer OpenID Connect over OAuth to ensure you know who is behind the request, not just what app is calling.
- Short-Lived JWTs: Limit the lifespan of JSON Web Tokens to 15 minutes. Implement Refresh Token Rotation to ensure that stolen tokens are invalidated the moment a new one is requested.
Mutual TLS (mTLS) for B2B APIs
For service-to-service communication, especially in microservices, standard TLS is insufficient. mTLS requires the client to present a certificate to the server, creating a two-way trust bond.
- Key Takeaway: mTLS effectively eliminates the risk of Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks within your internal network.
3. Mastering Authorization: Blocking BOLA and BOPLA
Authorization is where most modern breaches occur. Authentication says “You are User A,” but Authorization says “User A can only see Order #505.”
Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA) Implementation
BOLA occurs when a user changes /api/v1/orders/505 to /api/v1/orders/506 and succeeds.
- The Fix: Never trust the user-provided ID. Your database query should always look like:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_id = $1 AND owner_id = $current_user_id. - Experience Signal: We’ve seen developers rely on “obfuscated IDs” (like UUIDs) as a security measure. This is “security by obscurity” and does not replace actual authorization checks.
Broken Object Property Level Authorization (BOPLA)
BOPLA is the 2026 evolution of Mass Assignment. It happens when an API returns too much information (e.g., returning the is_admin flag in a user profile call).
- Solution: Use Data Transfer Objects (DTOs) to explicitly define which fields are returned to the client.
4. Traffic Management: Contextual Rate Limiting
Simple rate limiting (e.g., 100 requests per minute) is too blunt a tool for modern web development.
Cost-Based Throttling
Not all API calls are created equal. A “Search” call that triggers a heavy database join should “cost” more than a “Ping” call.
- Implementation: Assign a weight to each endpoint. Give users a “budget” of 1,000 credits. A Search costs 50; a Ping costs 1.
- Key Takeaway: This prevents “Resource Exhaustion” attacks where attackers crash your database with legally formatted but heavy queries.
5. Securing the AI-API Integration (The 2026 Frontier)
If your API feeds data into a Large Language Model (LLM), you have a new attack surface: Indirect Prompt Injection.
Prompt Injection Shielding
Attackers can place malicious instructions inside data stored in your database. When your API fetches that data and sends it to an LLM, the LLM executes the malicious instructions.
- The Blueprint: Treat LLM outputs as untrusted code. Use a “cleaner” API layer to validate that the AI’s response does not contain system-level commands or sensitive PII.
6. API Discovery and Shadow API Governance
You cannot secure what you don’t know exists. “Shadow APIs”—undocumented endpoints left by developers—are the leading cause of “untraceable” breaches.
Automated Inventory via Traffic Mirroring
Our data at infineural Technologies suggests that the average enterprise has 33% more APIs than their documentation shows.
- Actionable Step: Use traffic mirroring to send a copy of all network traffic to a discovery tool. This tool should automatically flag any endpoint (e.g.,
/debug/users) that isn’t in your official OpenAPI/Swagger spec.
7. The Secure CI/CD Pipeline: Shifting API Security Left
Security shouldn’t be a gateway at the end of the process; it should be integrated into the build.
Contract Testing
Use tools to ensure that any change to an API doesn’t break the “security contract.” If a developer accidentally adds a field to a response that isn’t in the DTO, the build should fail.
- Fuzz Testing: Integrate automated fuzzing into your pipeline to send malformed data to your API and check for unexpected crashes or data leaks.
8. GraphQL Specific Security: Solving the Depth Problem
GraphQL APIs require a different API Security Best Practices Guide than REST APIs. Because GraphQL allows users to define the shape of the response, it is vulnerable to Query Depth attacks.
Implementing Depth Limiting
An attacker can write a recursive query: user { friends { friends { friends … }}}. This will eventually crash the server.
- The Fix: Set a maximum depth for queries (e.g., max 5 levels).
- Key Takeaway: Use “Query Cost Analysis” to calculate the complexity of a GraphQL request before executing it.
9. Post-Breach Forensics: What to Log
If a breach occurs, your logs are your only map. Standard logs (IP and Timestamp) are useless for API forensics.
The API Forensic Log Checklist
- User Identifier: Not just the IP, but the authenticated User ID.
- Request/Response Metadata: Log the size of the response. A sudden jump from 2KB to 2MB responses is a sign of data exfiltration.
- Correlation IDs: Ensure every request has a unique ID that follows it through all microservices.
10. API Security Implementation Checklist (2026 Edition)
- [ ] Decommission TLS 1.2: Enforce TLS 1.3 exclusively.
- [ ] Remove API Keys from URLs: Move all credentials to the Authorization Header.
- [ ] Implement HSTS: Ensure browsers only interact with your API via HTTPS.
- [ ] Audit for Zombie APIs: Delete old versions (v1, v2) that are no longer supported.
- [ ] Sanitize Error Messages: Never return stack traces or database errors to the end user.
FAQ Section (People Also Ask)
1. What is the most common API security vulnerability? Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA) is the most frequent flaw, where an API fails to verify if a user has permission to access a specific resource ID.
2. Is an API Key enough for security? No, API keys are for identification, not secure authentication; you should use OAuth 2.0/OIDC for robust security.
3. What is the difference between BOLA and BOPLA? BOLA involves accessing a resource you don’t own, while BOPLA involves accessing specific properties (like an admin flag) within a resource you might otherwise be allowed to see.
4. How do I prevent Shadow APIs? Implement continuous API discovery through traffic mirroring to find undocumented endpoints that aren’t in your Swagger/OpenAPI files.
5. What is mTLS in API security? Mutual TLS is a protocol where both the client and server provide digital certificates to verify each other’s identity before communication begins.
6. Can a WAF protect against API logic attacks? Standard WAFs are poor at stopping logic attacks; you need an API-specific security layer that understands request context and user behavior.
7. Why is GraphQL more vulnerable than REST? GraphQL is not inherently less secure, but its flexibility allows attackers to craft highly complex queries that can cause DoS or excessive data exposure if not limited.
8. How do I secure APIs for AI models? Use prompt injection shields and treat all AI-generated output as untrusted data that must be sanitized before being returned to the user.
Secure Your Architecture with infineural Technologies
The complexity of modern web development means that a single oversight in your API logic can lead to a catastrophic breach. At infineural Technologies, we don’t just provide a list of rules—we provide the architectural oversight and AI-driven monitoring tools to ensure your APIs are “secure by design.”
Whether you are building a new microservices architecture or auditing a legacy system, our experts can help you implement the most advanced API Security Best Practices Guide strategies.
Talk to an Expert at infineural Technologies Today Download our 2026 API Security Roadmap